Call Experts
+91 93631 75000

Code on Wages
-
Factories Act, 1948
-
Mines Act, 1951
-
Dock Workers ( safety, Health and Welfare Act, 1986
-
The Building and other Workers (Regulation of
-
Employment and Conditions of Service) Act, 1996
-
The Plantations Labour Act, 1951;
-
The Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act,1970
-
The Inter-State Migrant workmen (Regulation of Employment and
Conditions of Service) Act, 1979; -
The Working Journalist and other News Paper Employees (Conditions of Service and Occupational Safety, Health &Working Condition Misc. Provision) Act, 1955;
-
The Working Journalist (Fixation of rates of wages) Act, 1958;
-
The Motor Transport Workers Act, 1961;
-
Sales Promotion Employees (Condition of Service) Act, 1976;
-
The Beedi and Cigar Workers (Conditions of Employment) Act, 1966
-
The Cine Workers and Cinema Theatre Workers Act, 1981
}
Occupational Safety, Health &Working Condition
Code 2020
Existing Legislation
New Legislation
Key Changes
-
Code provides single registration for an establishment instead of multiple registrations. This will design a centralized database and develop an ease of doing business.
-
Appointment letter made Statutory.
-
Working Hours For Women: Working Hours for Women as per this new proviso female workers/women can work during night shifts with their consent. Also, the time slot for such night shift shall be from 7 p.m. and before 6 a.m., which shall also be approved by the central or state govt.
-
Rights and duties of employees and employers: Rights and duties laid down in the Code for employees too, employees shall take care of their own health, shall comply with specified safety and health measures, shall report unsafe situations to the inspector.
-
Offences and Penalties: Under the Code, an offence which leads to the death of an employee will be punishable with imprisonment of up to two years, or a fine up to five lakh rupee or, both. Further, the court (Chief Inspector-cum-Facilitator or Inspector-cum-Facilitator or an officer of the appropriate Government or a person authorised to discharge any duty or to exercise any powers under this Code) has been granted a discretionary power wherein, it may direct that at least 50% of such fine be given as compensation to the heirs of the victim. The Code further states that where no penalty has been laid down for violation of the provision of the Code by the employer, the employer will be penalised with a fine between two to three lakh rupees. And where the employee violates any provisions of the Code, he will be subject to a fine of up to Rs. 10,000.
-
The appropriate government for the factory governed by the central government will be central government, including establishment of contractors for the purposes of such establishment. In other cases the concerned State Government where it is situated.
-
The code has also covered Audiovisual production' including feature films, non-feature films, television, web-based serials, talk shows, reality shows etc and under the new definition of Audio Visual- Worker” singer, news reader, dancer, stunt person, technical, artist and work like supervisory etc has been covered subject to some wages ceiling to be notified by the central government.
-
The definition of Contract Labour has been modified and includes inter-State migrant worker but excludes part-time employees, regularly employed n mutually accepted standards of the conditions of employment and entitled to Social Security benefits.
-
The new definition of Core Activity provides that activity for which establishment is set-up and
-
other activity like housekeeping, Security, canteen etc not to be treated as core activity.
-
Principal employer to provide welfare facilities, where the contract labour is deployed.
-
Principal employer shall be liable to make payment of wages to the contract labour deployed by him
-
The work hours for different classes of establishment and employees shall be as per the rules prescribed by central or state government. Further, in relation to overtime work, an employee shall be paid twice the rate of daily wages. The code in regard to leaves states that no employee shall work for more than 6 days a week, however, an exception has been provided for motor transport workers.
-
Definition of “ Employee” has been incorporated and includes person doing any skilled, semi- skilled or unskilled, manual, operational, supervisory, managerial, administrative, technical or clerical work for hire or reward.
-
As per new definition of “Employer” a person who employs, whether directly or through any person or on his behalf, or on behalf of any person, one or more employees in his establishment. and would be
-
Head of the department
-
Occupier of the factory
-
Manager of the factory under clause (f) of sub-section (1) of sec 7 of the Factories Act.
-
Owner of the mine, agent or manager.
-
The person who, or the authority which has ultimate control over the affairs of the establishment and where the said affairs are entrusted to a manager or managing director, such manager or managing director;
-
Contractor; and legal representative of a deceased employer.
-
The definition of the “Factory” has been revised under section 2 (w) and threshold limit of employees is now 20 in case of use of power and 40 in case without power and has specifically excludes, hotels, restaurant, eating place, Electronic Data Processing Unit or a Computer Unit etc.
-
The definition of "hazardous substance" provides any substance, has potential to cause physical or health hazards to human being, other living creatures etc
-
A new definition “Industrial premises” provides a premises in which any industry, trade, business etc is being carried on with or without the aid of power includes a godown.
-
Definition of “Inter State Migrant worker” has been modified and ceiling limit of Rs 18000/- has been introduced.
-
Definition of "machinery" has been inserted includes any article or combination of articles assembled, used or intended to be used for converting any form of energy to perform work.
-
Definition of "manufacturing process" has been taken from Factory Act and provides such other processes as the central Government may notified.
-
Definition of “metro railways” has been added and Metro railways has been treated as railways.
-
Definition of “newspaper establishment” has been drastically changed and has covered all type of establishment carried on by individual, partners, created firm, body corporate subsidiaries of a common holding company etc.
-
Definition of the “Occupier” has been amended and instead of clause a, b and c in second proviso, a consolidated definition has been given.
-
Definition of the “principal employer” has been modified to the extent that the manager has been excluded from the definition of the principal employer.
-
Definition of the “producer” has been added means a person who is making arrangement for necessary of production is also included.
-
Definition of “Sales Promotion Employees” has been revised including a persons in supervisory capacity, managerial, administrative capacity getting salary up to Rs 18000/- per month or as may be notified by the Central Government from time to time.
-
Definition of “worker” has been revised and includes persons in supervisory capacity and working journalists, sales promotion employees getting salary up to Rs. 18000/- per month or as may be notified by the Central Government from time to time
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & WORKING CONDITION CODE 2020
Bill Introduced in Lok Sabha on 28th November 2019

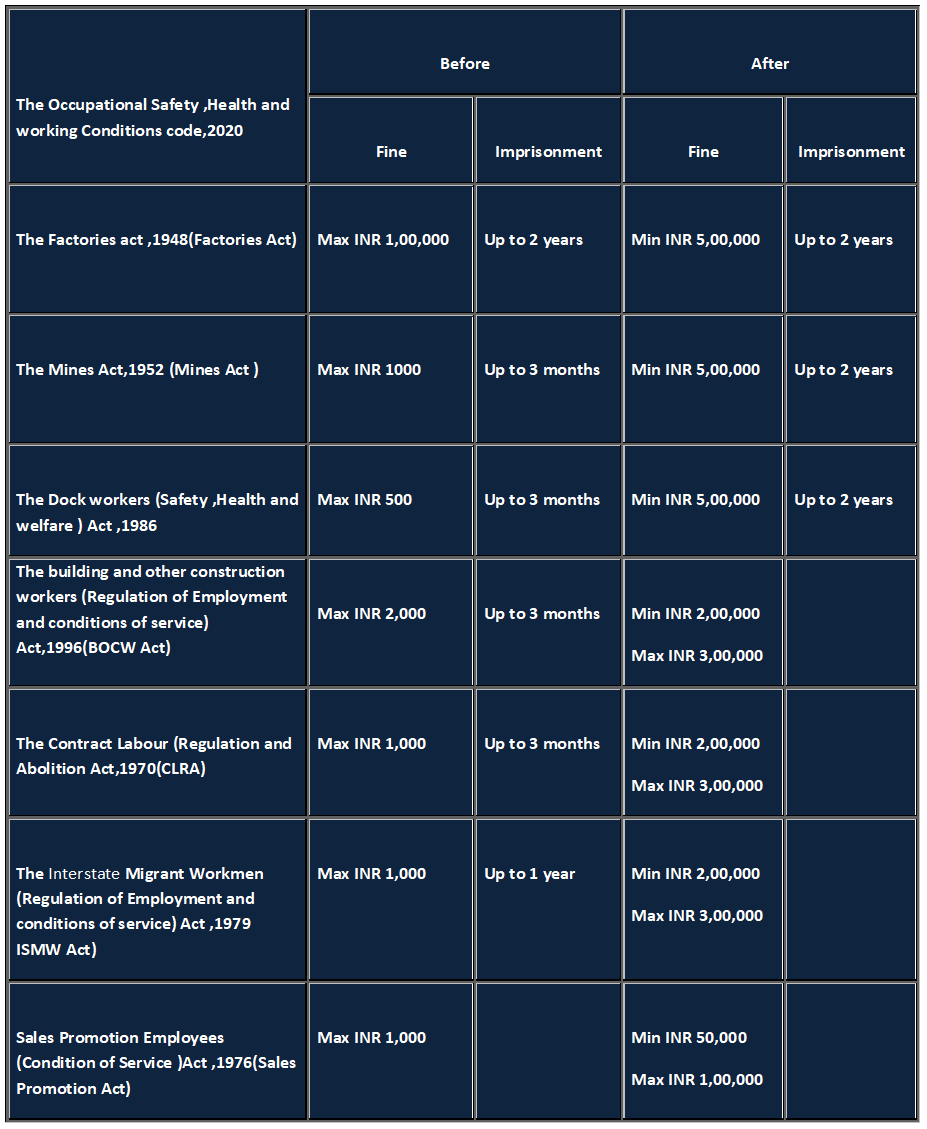
Note: Data sourcing from CII and Greyt HR - HR Conclave - July 2022
Non-Compliance Consequences Code On Wages,2019