Call Experts
+91 93631 75000

Social Security Code 2020
Bill Introduced in Lok Sabha on 11th December 2019


Code on Wages
-
The EPF and M.P. Act, 1952
-
The ESIC Act, 1948
-
The Maternity Benefit Act,1961
-
The Building and other Construction Worker Cess Act
-
The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
-
The Employees Exchange (Compulsory
-
Notification of Vacancies) Act, 1959
-
The Cine Workers Welfare Fund Act, 1981
-
The Unorganized Workers’ Social Security Act,
-
2008
-
Employees Compensation Act, 1923
}
Social Security Code 2020
Existing Legislation
New Legislation
Key Changes
Non-Compliance Consequences Code On Wages,2019
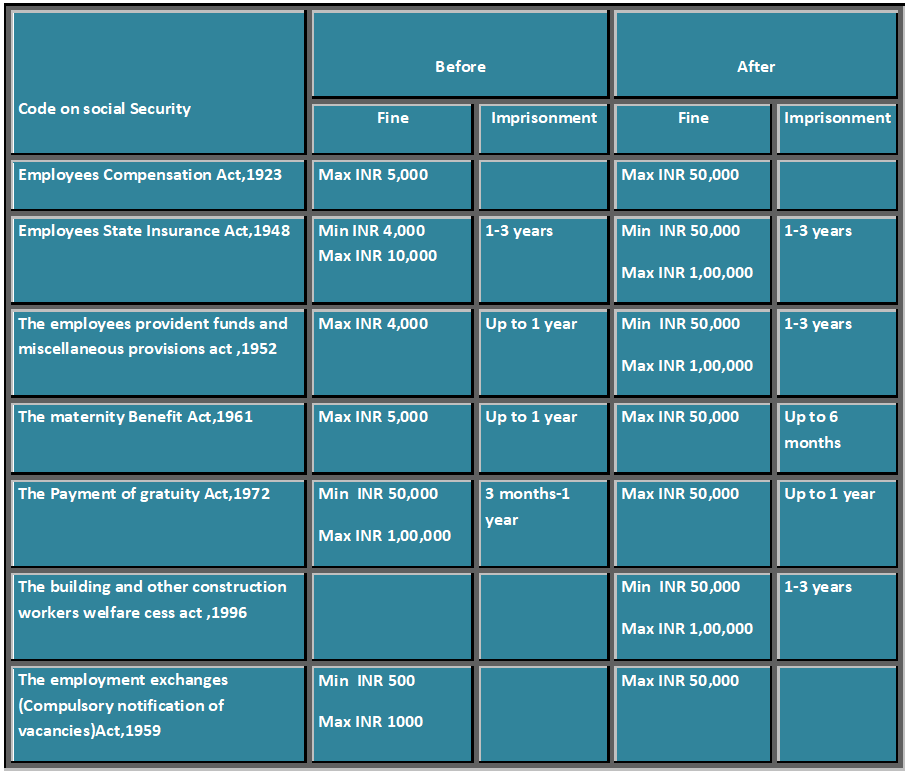
-
New Category of worker has been included in this code:-
-
Gig worker" means a person who performs work or participates in a work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of traditional employer- employee relationship.
-
Gig workers are in independent arrangement, freelancers, workers who are employed on project based work and short term work. Most commonly, platform based work where workers earn money by providing specific services, including food delivery services.
-
“Platform worker" means a person engaged in or undertaking platform work
-
Platform work" means a form of employment in which organisations or individuals use an online platform to access other organisations or individuals to solve specific problems or to provide specific services in exchange for payment.
-
There is no major difference in gig workers and platform workers. This is first time in India that application based assignments performed by many workers being recognized as employee-employer relationship.
-
Definition of wages has been revised:-
-
the First part includes all salary components express in terms of money are capable of being
-
so expressed like basic salary, all reimbursements, all allowances, all benefits.
-
Second part of the definition provide specific exclusion like:- Bonus payable under any law, Conveyance allowance, House rent allowance, Overtime Allowance, House Accommodation, Supply of light water medical attendance, other amenities/ service excluded by a General or special order of the appropriate government, Commission, contribution to provident fund/pension, Any sum paid to defray special expenses, Gratuity, Retrenchment Compensation, Remuneration payable under any award or settlement between the parties.
-
The Third part of the definition provides that the total excluded components should not exceed 50% of the total remuneration. The third part of the definition provide limit as the definition very clearly specifies the list of exclusions so anything which is paid to the employees other than the exclusion would be covered and within this specific exclusion the limit cannot be more than 50%.
-
Impact: As of now HRA is a part of minimum wages and with the implementation of code HRA will not be part of minimum wages will have an implication of the EPF contribution.
-
THE EMPLOYEES PROVIDENT FUND SCHEME
-
Major reforms in the Employees Provident Fund Scheme is incorporation of limitation
-
period of five years for initiation and two years for concluding enquiries.
-
Aadhaar based registration is mandated.
-
All establishments having 20 or more workers come under the purview of EPF, earlier it
-
was applicable only on those establishments included in the schedule.
-
Systems has been designed for covering the category self-employed or any other category under the purview of EPF scheme.
-
Increase penalty amount from 10,000 to 1,00,000 and imprisonment of one to three years on deduction of employee contribution from salary and non-depositing.
-
Subsequent failure to pay contributions attracts imprisonment of two to five years and fine of three lakh rupees.
-
EMPLOYEES STATE INSURANCE SCHEME
-
If employer and majority employees agree then voluntary registration has been allowed under the code and ESI scheme will be applicable. Further, government can extend ESI scheme to any hazardous occupation also even if a single employee is employed.
-
The Facility of ESI would be available to all 740 districts.
-
Gig workers and unorganized sectors will also able to link with ESIC.
-
Plantation workers will also fall under the purview of ESI.
-
If any employer fails to pay ESI contributions, even then ESI has to pass on the benefits to the employee which ESIC can recover it from the employer to the extent of the capitalised value of the benefit net of any payment of contribution amount, interest and damages payable by the employer.
-
Gratuity
-
Permanent employees would be eligible for gratuity after completion of five years as presently exist under the Act, while fixed-term employees will have no such criteria, such employees will be paid on the basis of their tenure of employment with one organization. Code has fixed different threshold with respect to eligibility for gratuity of permanent and fixed term employees.
-
The threshold Gratuity period for working journalists reduces from five years to three years.
-
EMPLOYMENT INFORMATION AND MONITORING
-
Employers, job seekers looking for vocational guidance, career counseling, self employment
-
requires to register with career centres.
-
All establishment except some exclusion like agriculture, domestic service, employment less than ninety days etc required to notify the vacancies to career centres electronically or otherwise.
-
Filing the return by the employer to the concerned career centre.
-
Maternity Benefit
-
Every woman is entitled to medical bonus of up to Rs 3,500 where pre-natal confinement and post-natal care is not provided by employer whose upper limit can be amend by the Central government upto Rs 20000/- , this upper limit of Rs 20000 has been removed under the code.
-
EMPLOYEE'S COMPENSATION ACT, 1923, BUILDING AND OTHER CONSTRUCTION WORKERS, THE UNORGANIZED WORKERS' SOCIAL SECURITY ACT (2008), ETC.
-
Creation of social security boards for unorganized workers.
-
Coverage of gig, platform workers and unorganized workers under the ambit of social security
-
Scheme.
-
Code to expand the sources of the fund for schemes to include funds from corporate social responsibility or any other source as may be specified in the scheme and also contains enabling provision for constituting the special purpose vehicle for the purpose of implementation of schemes for unorganized workers.
-
Bill also makes the provisions for registration of all three categories of workers - gig workers platform workers and unorganized workers.
-
Contribution from an aggregator will be at a rate notified by the government which can fall between 1-2% of the annual turnover of the aggregators. However, the maximum limit of such contribution fixed @ 5% of the amount paid or payable by an aggregator to gig workers and platform workers.
-
General Change
-
Renaming the designation of Inspector as Inspector cum Facilitator who is expected to supply information and give advice to employers and workers concerning the most effective means of complying with the provisions of the proposed Code.
Note: Data sourcing from CII and Greyt HR - HR Conclave - July 2022