Call Experts
+91 93631 75000


Code on Wages
-
The Minimum Wages Act, 1948
-
The Payment of Wages Act, 1936
-
The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
-
The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
}
Code on Wages 2019
Existing Legislation
New Legislation
Key Changes
Non-Compliance Consequences Code On Wages,2019
-
Sec 2(g) defines ‘contract labour’ ( specifically includes inter-state migrant workmen and excludes the persons who are regularly employed )
-
Common definition for ‘wages’ for all the four existing laws [Sec 2(y)]
-
Certain allowances, excluded for Minimum Wages and Bonus but included for Payment of Wages and Equal Remuneration (Convey, HRA, Remuneration under Settlement & Award and OT)
-
A cap – 50 % - fixed for ‘excluded components’
-
HRA – No more part of minimum wages
-
No employer shall pay to any employee wages less than the minimum rates of wages notified by the appropriate Government ( Sec 5 )
-
The Central Government will fix the floor wages ( Sec 9 )
-
Rate of minimum wages fixed by the appropriate Government shall not be less than the floor wage
-
-
National floor wages shall be revised every 5 years [Rule 11 (4)]
-
Payment of Wages Act – Ceiling of Rs 24000/- removed now – the Act applies to all
-
In case of separation, including resignation, the settlement is to be made within the next two working days
-
Payment of Bonus chapter shall apply to the establishments in which 20 or more persons are or were employed on any day during an accounting year ( Sec 41(2) )
-
The Code is silent about the applicability if the threshold limit falls below subsequently
-
Wages ceiling for eligibility for Bonus : To be fixed by the Appropriate Governments
-
Wages ceiling for calculation of Bonus : To be fixed by the Appropriate Governments
-
-
Contractor’s payment shall be ensured by Company before the contractor makes the payment of wages to his employees (Rule 54)
-
In case of non-payment of minimum bonus to the contract worker, company should pay the same. But no specification about recovery from contractor - Rule 56
-
The appropriate government shall fix ( Sec 13 )
-
the hours of work which constitutes a normal working day;
-
define the intervals in a working day;
-
provide for a rest day in every 7 days;
-
if the employee is called to work on a rest day or works beyond normal hours, then payment is to be made at overtime rates (i.e. twice the normal rate)
-
-
Central Rules (Draft) :
Daily hours shall be maximum of 9 hours (Rule 6) -
Spread over in normal circumstances 12 hours and in case of overtime shall not exceed 16 hours. (Rule 9)
-
Overtime shall be allowed or required, only in case of sudden spurt of business (Rule 9).
-
One day weekly holiday to be given after end of 6 working days. (Rule 7).
-
-
Employer shall fix the wage period and it shall not be more than one month ( Sec 16 ):
-
Daily wage shall be paid by the end of the day
-
Weekly wage shall be paid on the last working day of the week
-
Fortnightly wage shall be paid within 2 days after the end of the period
-
Monthly wages shall be paid within 7 days after the month
-
-
Minimum wage applies to employees as well as workers
-
The appropriate Governments can fix the rates of minimum wages
-
Definitions of Unskilled, Semiskilled, Skilled and Highly Skilled Occupations are introduced in the Rules [Rule 2 (j), (t) (u) & (v)]
-
Geographical Areas classified as metropolitan, non-metropolitan and rural areas (Rule 4)
-
‘Metropolitan’ means 40 lakhs and above population area - Rule 2(m)
-
‘Non-metropolitan’ means above 10 lakhs but below 40 lakhs - Rule 2(n)
-
‘Rural area’ means other than metro and non-metro - Rule 2(q).
-
-
Only authorized deductions are to be made ( Sec 18 )
-
Wage slip shall be issued
-
Total amount of deduction in any wage period from the wages of employed person shall not exceed 50% (Currently in case of co-operative Society – 75%)
-
Recovery of advance can be done without any stipulated time but with one condition ie. Recovery can't go more than 50% on any wage period (Rule 19). (Currently in TN – 12 months)
-
Deduction for damage or loss shall be done only with specified procedure. Explain personally and intimate in writing within 15 days from the date of such deduction (Rule 18)
-
Undisbursed due ( unpaid accumulation) period is 6 months - Rule 46
-
Amount to be settled within 15 days from the date of last day of due period. (Rule 46(1))
-
Amount to be deposited through bank transfer or DD - Rule 46 (2)
-
-
If the undisbursed amount remains unclaimed for a period of seven years, the same shall be dealt in the manner as directed by the Central Government - Rule 47(4)
-
Mode of payment of bonus - Only by giving bank credit
-
Disqualification for bonus : ‘conviction for sexual harassment’ added
-
Differentiates ‘employee’ (Sec 2(k)) and ‘worker’ ( Sec 2(z))
-
Sec 2(f) defines who ‘a contractor’ is ( almost on par with the one in the existing CLRA Act )
-
Period of limitation is 3 years for claim.
-
Claim to be determined and in addition 10 times of such amount (MW, Bonus & Equal Wages)
-
-
Introduction of Web based inspection Scheme
-
The role of inspector is modified as Inspector-cum-facilitator
-
-
Wages shall be paid in current coin or currency notes or by cheque or by crediting wages in the bank a/c ( Sec 15 )
-
In case of complaint, Court can take cognizance directly from employee and the Registered Trade Union
-
Burden of Proof - lies with the employer
-
Enhanced Penalties for offence with the view of priority to compliance:
-
For the offence of non-payment for the first time : Rs 50000/- fine
-
For the subsequent offence : Rs 100000/- fine or 3 months or both
-
38. For the offence of non-payment for the first time : Rs 50000/- fine
-
For the subsequent offence : Rs 100000/- fine or 3 months or both
-
For non-maintenance / improper maintenance of records : Rs 10000/-
-
For any other non-compliance for the first time : Rs 20000/- fine
-
For the subsequent offence : Rs 40000/- fine or 1 month or both
-
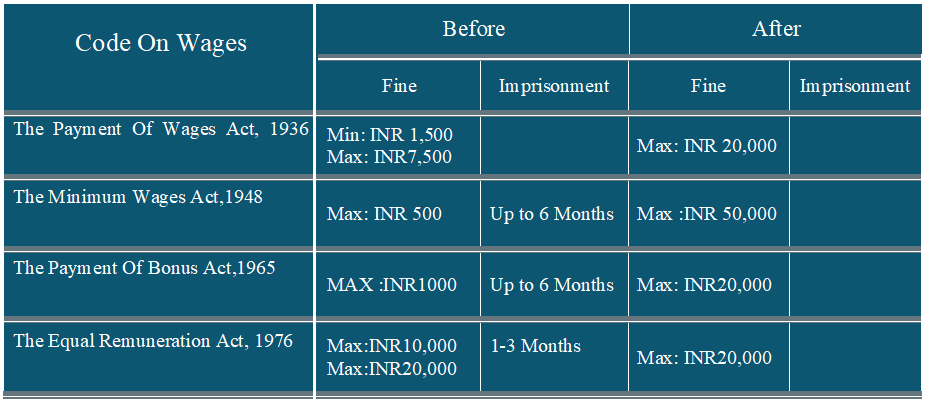
Note: Data sourcing from CII and Greyt HR - HR Conclave - July 2022

Code on Wages,2019
Bill passed in Lok Sabha (30th July 2019), Rajya Sabha (2nd August 2019) and Received President’s Assent on 8th August 2019, Draft Central Rules issued.